Information You Must Know in Order to Compute the Area Under the Normal Curve Over a Given Interval
Earlier you can solve for the surface area under a normal curve, you must be able to imagine what the area looks like. The best (albeit optional) way practise this is to make a sketch. For example, let's say you were give a z-score and were asked to find the expanse between that score and z = 0 (the mean). Your sketch might await like this:
Find an area from z = 0 to z = ?
There are seven ways your sketch could look, depending on what z-values you were given. Once yous have drawn your sketch, look at the pictures below. Click on the epitome that looks most like your sketch. The link will have you lot to a stride-by-footstep guide on how to discover the area nether a normal curve for that shape. Many of these as well have brusque videos showing the steps.
This video shows you how to discover the area under a normal curve for a tail (either a left or right tail):
Tin't see the video? Click here.
Choose One
Find an surface area under a normal curve from z = 0 to z = ?
Find an area in 1 tailed distribution (left or right)
area betwixt two z scores on aforementioned side
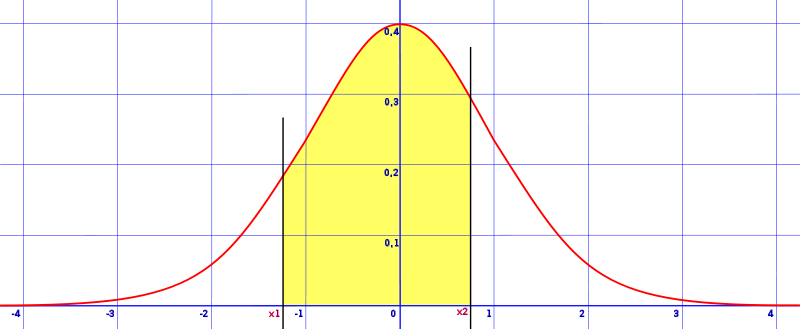
expanse between two z values on opposite sides of hateful
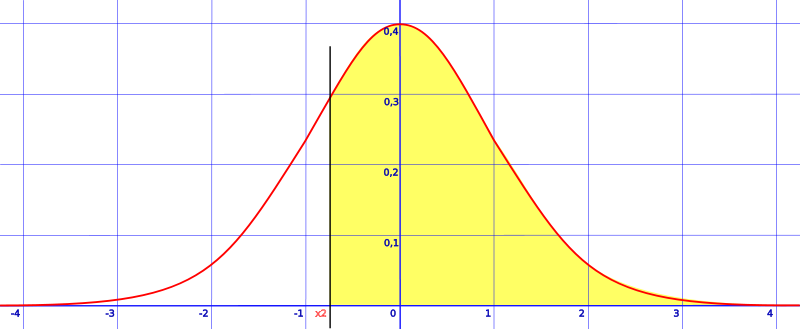
area left of a z score (z is greater than the mean)
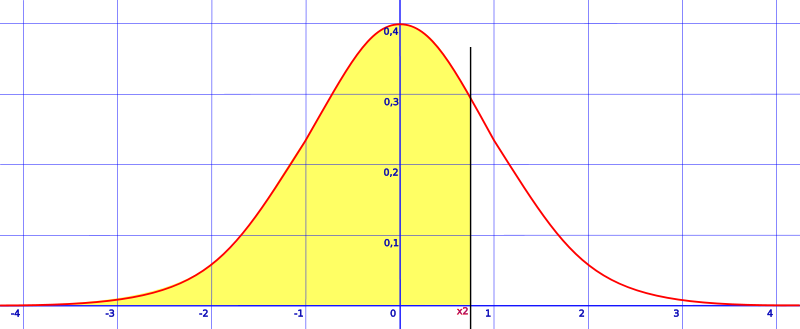
area to the right of a z score (z is greater than the mean)
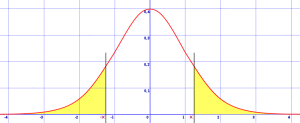
area under a two tailed normal curve
Tip: Drawing sketches in probability and statistics isn't merely limited to normal distribution curves. If you go used to making a sketch, y'all'll besides have an easier time with creating complicated graphs (similar Contingency Table: What is it used for?.
Find an area under a normal curve from z=0 to z=?

Detect an expanse from z = 0 to z = ?
How to discover the area under a curve (between 0 and any z-score)
You can wait up numbers in the z-tabular array, like 0.92 or 1.32. The values you get from the table give y'all How to Calculate Percentages: Simple Steps for the area under a curve in decimal form. For example, a table value of .6700 is are surface area of 67%.
Note on using the tabular array: In lodge to look up a z-score in the table, you have to dissever upwards your z-value at the tenths place. For example, to look up 1.32 y'all would wait upwardly 1.3 then look at .02. Encounter the case below for a visual on what finding the intersection looks similar. If you demand more help, watch the video on this z-table folio.

Normal Distribution curve
Pace i: Await in the z-table for the given z-score by finding the intersection. For instance, if you lot are asked to find the area betwixt 0 and 0.46, look up 0.46.* The tabular array below illustrates the result for 0.46 (0.4 in the left mitt column and 0.06 in the tiptop row. the intersection is .1772).
| z | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.0000 | 0.0040 | 0.0080 | 0.0120 | 0.0160 | 0.0199 | 0.0239 | 0.0279 | 0.0319 | 0.0359 |
| 0.1 | 0.0398 | 0.0438 | 0.0478 | 0.0517 | 0.0557 | 0.0596 | 0.0636 | 0.0675 | 0.0714 | 0.0753 |
| 0.2 | 0.0793 | 0.0832 | 0.0871 | 0.0910 | 0.0948 | 0.0987 | 0.1026 | 0.1064 | 0.1103 | 0.1141 |
| 0.3 | 0.1179 | 0.1217 | 0.1255 | 0.1293 | 0.1331 | 0.1368 | 0.1406 | 0.1443 | 0.1480 | 0.1517 |
| 0.4 | 0.1554 | 0.1591 | 0.1628 | 0.1664 | 0.1700 | 0.1736 | 0.1772 | 0.1808 | 0.1844 | 0.1879 |
| 0.v | 0.1915 | 0.1950 | 0.1985 | 0.2019 | 0.2054 | 0.2088 | 0.2123 | 0.2157 | 0.2190 | 0.2224 |
That'southward it!
*Notation. Because the graphs are symmetrical, yous can ignore the negative z-scores and but look up their positive counterparts. For example, if you are asked for the surface area of 0 to -0.46, but wait up 0.46.
Check out our YouTube channel for hundreds of statistics help videos!
References
Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 31st ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 536 and 571, 2002.
Agresti A. (1990) Categorical Data Assay. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Everitt, B. S.; Skrondal, A. (2010), The Cambridge Lexicon of Statistics, Cambridge University Press.
Gonick, Fifty. (1993). The Drawing Guide to Statistics. HarperPerennial.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Need help with a homework or test question? With Chegg Written report, y'all can go step-by-step solutions to your questions from an expert in the field. Your first thirty minutes with a Chegg tutor is costless!
Comments? Need to postal service a correction? Please mail service a comment on our Facebook folio .
whitakerphers1985.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/normal-distributions/find-the-area-under-a-normal-curve/
0 Response to "Information You Must Know in Order to Compute the Area Under the Normal Curve Over a Given Interval"
Post a Comment